Market Entry Strategies sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with an american high school hip style and brimming with originality from the outset.
As businesses navigate the complexities of expanding into new markets, understanding the various strategies available is crucial for success. From exporting to joint ventures, the right approach can make or break a company’s entry into unfamiliar territory.
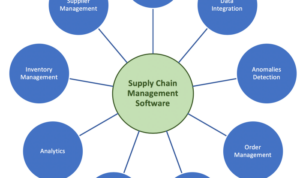
Market Entry Strategies Overview

Market entry strategies refer to the various methods and approaches that businesses use to enter a new market and establish their presence. These strategies are crucial in determining the success and sustainability of a business in a new market.
Examples of Market Entry Strategies
- Exporting: Selling products or services to customers in a foreign market without establishing a physical presence.
- Licensing: Allowing a foreign company to use your intellectual property or technology in exchange for royalties.
- Joint Venture: Partnering with a local company in the foreign market to share resources, risks, and expertise.
- Franchising: Allowing a local individual or company to operate under your brand name and business model.
Importance of Selecting the Right Market Entry Strategy
Choosing the appropriate market entry strategy is crucial for the success of a business in a new market. The right strategy can help businesses navigate challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and establish a strong presence. It is essential to consider factors such as market conditions, competition, regulatory environment, and resources when selecting a market entry strategy.
Types of Market Entry Strategies
In the world of business, there are various ways for companies to enter new markets. Each strategy comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages, depending on the specific goals and circumstances of the business.
Exporting
Exporting involves selling goods and services produced in one country to customers in another country. This can be done directly by the company or through intermediaries like distributors. Some advantages of exporting include low risk and cost-effective entry, while disadvantages may include limited control over distribution and potential cultural barriers.
Licensing
Licensing allows a company to grant the rights to produce and sell its products or use its intellectual property to another company in a foreign market. The advantage of licensing is the ability to expand without significant investment, but the downside is the risk of losing control over quality and brand image.
Franchising
Franchising is a strategy where a company allows another party to operate a business using its name and business model in exchange for fees and royalties. The main advantage of franchising is rapid expansion with reduced capital investment, but the challenge lies in maintaining brand consistency and quality across different locations.
Joint Ventures
Joint ventures involve two or more companies coming together to form a new entity and share resources, risks, and rewards in a foreign market. The benefit of joint ventures is access to local expertise and resources, but conflicts may arise due to differing objectives and management styles.
Wholly Owned Subsidiaries
Wholly owned subsidiaries are entities established by a parent company in a foreign market, giving full control over operations and decision-making. The advantage is complete control and alignment with the parent company’s goals, but the downside is the high cost and risk involved in setting up and managing the subsidiary.
Real-World Examples
– Coca-Cola successfully entered the Chinese market through joint ventures with local companies.
– McDonald’s has expanded globally through franchising, allowing local entrepreneurs to operate its restaurants.
– Apple uses licensing agreements to allow third-party manufacturers to produce and sell accessories for its products.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Market Entry Strategy
When deciding on a market entry strategy, businesses must take into account various key factors that can significantly impact their success in a new market. These factors include market characteristics, competition, legal regulations, and cultural differences. By carefully evaluating these aspects, companies can determine the most suitable market entry strategy that aligns with their goals and objectives.
Market Characteristics, Market Entry Strategies
Market characteristics such as size, growth potential, and customer preferences play a crucial role in determining the appropriate market entry strategy. Understanding the demand for products or services in the target market, as well as the level of competition and market saturation, is essential for making informed decisions. Companies should conduct thorough market research to identify opportunities and challenges before entering a new market.
Competition
Assessing the competitive landscape is vital when choosing a market entry strategy. Companies need to analyze the strength and positioning of competitors, as well as their market share and pricing strategies. By understanding the competitive environment, businesses can develop effective strategies to differentiate themselves and gain a competitive advantage in the new market.
Legal Regulations
Legal regulations and compliance requirements vary across different markets and industries. Companies need to consider the legal framework governing business operations, trade policies, intellectual property rights, and other regulatory factors that may impact their market entry strategy. Failure to comply with legal requirements can lead to costly penalties and reputational damage, highlighting the importance of thorough due diligence.
Cultural Differences
Cultural differences can significantly influence consumer behavior, marketing strategies, and business practices in a new market. Companies must adapt their products, messaging, and operations to align with the cultural norms and preferences of the target market. Building strong relationships with local partners and stakeholders can help businesses navigate cultural nuances and establish credibility and trust with customers.
Market Entry Strategies in Different Industries
When it comes to entering new markets, different industries have unique characteristics that influence the choice of market entry strategies. Let’s explore how market entry strategies vary across industries such as technology, healthcare, consumer goods, and automotive.
Technology Industry
In the technology industry, companies often opt for direct investment strategies such as setting up subsidiaries or joint ventures in new markets to establish a physical presence. This helps in building relationships with local partners and customers, as well as gaining insights into market trends and consumer preferences.
Healthcare Industry
For healthcare companies, market entry strategies may involve partnerships with local hospitals or healthcare providers to distribute products and services effectively. Regulatory challenges and compliance requirements play a significant role in shaping market entry strategies in this industry.
Consumer Goods Industry
In the consumer goods industry, companies often focus on building brand awareness and distribution networks in new markets. Strategies such as licensing agreements or franchising can help companies expand their reach quickly and efficiently.
Automotive Industry
Automotive companies may choose to establish manufacturing facilities or distribution centers in new markets to reduce transportation costs and meet local demand effectively. Strategic partnerships with local suppliers or distributors can also play a crucial role in market entry strategies in the automotive industry.