Decentralized apps, or DApps, are taking the tech world by storm with their innovative approach to applications. Imagine a world where control is in the hands of users, not centralized entities – that’s the power of DApps.
As we dive deeper into the realm of decentralized apps, we uncover a universe where transparency, security, and efficiency reign supreme. Join us on this journey to explore the wonders of DApps and discover how they are reshaping the digital landscape.
Introduction to Decentralized Apps (DApps)
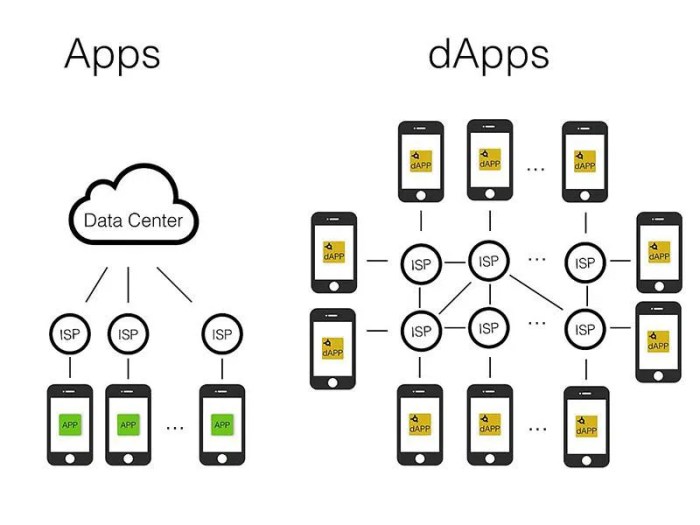
Decentralized Apps, or DApps, are applications that run on a decentralized network, typically utilizing blockchain technology. Unlike traditional centralized applications that rely on a single point of control, DApps operate on a peer-to-peer network, ensuring transparency, security, and immutability.
Fundamental Difference between Centralized Apps and DApps
In centralized apps, data and control are housed on a single server or entity, making them vulnerable to hacking, censorship, and data manipulation. On the other hand, DApps distribute data and control across multiple nodes on a decentralized network, eliminating the need for intermediaries and providing greater resilience against attacks.
Benefits of DApps over Traditional Centralized Applications
- DApps promote transparency and trust by allowing users to verify transactions on the blockchain.
- They offer greater security through cryptographic techniques and decentralized consensus mechanisms.
- DApps enable peer-to-peer interactions without the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
- They provide immutability of data, ensuring that once recorded on the blockchain, information cannot be altered or deleted.
- DApps foster innovation by allowing developers to create decentralized solutions that are resistant to censorship and control.
Architecture of Decentralized Apps
Decentralized apps, or DApps, have a unique architecture that sets them apart from traditional centralized applications. In a decentralized app, data is not stored on a single central server but is rather distributed across a network of computers, making them more secure and resilient to attacks.
Role of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts play a crucial role in the functioning of DApps. These self-executing contracts are stored on the blockchain and automatically enforce the terms of an agreement when certain conditions are met. This eliminates the need for intermediaries and ensures transparency and trust in transactions.
Data Storage and Processing, Decentralized apps
In DApps, data storage and processing differ significantly from centralized apps. Instead of relying on a single server, data is stored across multiple nodes in the network, ensuring redundancy and preventing a single point of failure. Additionally, data processing is carried out by the network as a whole through a consensus mechanism, such as proof of work or proof of stake, rather than a central authority.
Development of Decentralized Apps
Decentralized apps, or DApps, are gaining popularity in the tech world due to their decentralized nature. Let’s dive into the development process of these innovative applications.
Programming Languages for DApp Development
When it comes to developing DApps, developers commonly use programming languages like Solidity, which is specifically designed for creating smart contracts on blockchain platforms such as Ethereum. Other languages like Rust and JavaScript are also utilized for DApp development to enhance functionality and compatibility with different blockchain networks.
Deploying a DApp on a Blockchain Platform
Deploying a decentralized app on a blockchain platform involves several steps. First, developers need to write the smart contracts that define the logic of the DApp. Once the smart contracts are ready, they are compiled and deployed on the blockchain network. This deployment process ensures that the DApp is securely stored and executed on the blockchain, allowing users to interact with it in a decentralized manner.
Challenges Faced by DApp Developers
Developing DApps comes with its own set of challenges. One major challenge is ensuring the security of the smart contracts to prevent vulnerabilities and potential exploits. Additionally, scalability issues can arise when trying to accommodate a large number of users on the blockchain network. To overcome these challenges, developers conduct thorough testing, implement security best practices, and explore scalability solutions like layer 2 protocols and sidechains.
Use Cases and Industries for Decentralized Apps

Decentralized apps, or DApps, are revolutionizing various industries by providing a transparent, secure, and efficient way to interact and transact. Let’s explore some examples of industries that are benefiting from using DApps and how they are disrupting traditional business models.
Finance
- Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms are transforming the way people access financial services, such as lending, borrowing, and trading, without the need for intermediaries.
- Smart contracts on blockchain networks enable automated, secure, and transparent transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and increasing efficiency in financial processes.
- Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are used as a means of exchange and store of value, providing an alternative to traditional fiat currencies.
Supply Chain
- DApps are being used to track and trace products throughout the supply chain, ensuring authenticity, quality, and compliance with regulations.
- Smart contracts facilitate automated payments and agreements between different parties in the supply chain, reducing delays and disputes.
- Blockchain technology enhances transparency and visibility in supply chain operations, leading to increased trust among stakeholders.
Healthcare
- Decentralized healthcare platforms are improving data management, patient privacy, and interoperability of health records among healthcare providers.
- Patients have more control over their health data and can securely share it with authorized parties, enhancing collaboration and decision-making in healthcare delivery.
- Smart contracts ensure compliance with data protection regulations and streamline processes like insurance claims and medical billing.
Security and Governance in Decentralized Apps
Decentralized Apps (DApps) are designed with security and governance in mind to ensure data integrity and user privacy. Let’s delve into the key aspects of security and governance in DApps.
Security Features of DApps
- Distributed Ledger Technology: DApps leverage blockchain technology to store data across a network of nodes, enhancing security through decentralization.
- Smart Contracts: These self-executing contracts facilitate trustless transactions and automate processes, reducing the risk of fraud or manipulation.
- Cryptography: DApps use cryptographic algorithms to secure data transmission and storage, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Immutable Records: Data stored on the blockchain is tamper-proof, ensuring the integrity of transactions and creating a transparent audit trail.
Decentralized Governance in DApps
- Decentralized Decision-Making: DApps allow users to participate in the governance process through voting mechanisms, ensuring a fair and transparent system of governance.
- Token-based Governance: Some DApps utilize tokens to enable stakeholders to vote on proposals and influence the direction of the platform, fostering community engagement.
- Transparent Governance Processes: Governance decisions and changes to the protocol are recorded on the blockchain, providing visibility and accountability to all participants.
Consensus Mechanisms in DApps
- Proof of Work (PoW): PoW requires participants to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions, ensuring security through computational work.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): PoS involves validators staking their tokens to secure the network and validate transactions, incentivizing good behavior and penalizing malicious actors.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): DPoS relies on elected delegates to validate transactions and make governance decisions, enhancing scalability and efficiency in DApps.