Supply chain management is like orchestrating a symphony of efficiency and innovation in the business world. Dive into this dynamic realm where strategies, technology, and risk management play a crucial role in shaping the success of operations.
Overview of Supply Chain Management
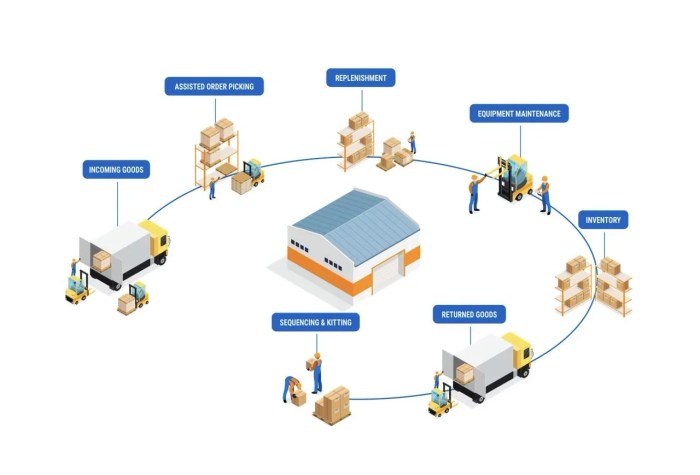
Supply chain management is the coordination and management of the flow of goods, services, information, and finances from the initial supplier to the end customer. It plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of businesses and maximizing efficiency.
Key Components of a Supply Chain
- Suppliers: The companies or individuals that provide the necessary inputs for production.
- Manufacturers: Entities that transform raw materials into finished products.
- Distributors: Organizations responsible for delivering products to customers.
- Retailers: Businesses that sell goods directly to consumers.
Role of Supply Chain Management in Efficiency
Supply chain management helps in optimizing processes, reducing costs, and improving customer satisfaction. By managing inventory levels, transportation, and warehousing efficiently, businesses can enhance their competitiveness in the market.
Supply Chain Strategies
In the world of supply chain management, companies must carefully consider and choose the most suitable strategy to ensure efficient operations and customer satisfaction. Three common supply chain strategies include lean, agile, and responsive approaches.
Lean Supply Chain Strategy
A lean supply chain strategy focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency in every aspect of the supply chain. Companies adopting this strategy strive to reduce excess inventory, streamline processes, and cut down on unnecessary costs. By implementing lean principles, organizations can achieve cost savings and improve overall productivity.
Agile Supply Chain Strategy
An agile supply chain strategy emphasizes flexibility and adaptability to quickly respond to changes in demand or market conditions. Companies following this approach prioritize speed and responsiveness, allowing them to adjust production schedules, inventory levels, and distribution channels in real-time. This strategy is ideal for industries with rapidly changing customer preferences or unpredictable market trends.
Responsive Supply Chain Strategy
A responsive supply chain strategy combines elements of both lean and agile approaches to create a dynamic and customer-centric supply chain. Companies utilizing this strategy focus on delivering customized products or services quickly while maintaining cost efficiency. By leveraging technology and data analytics, organizations can anticipate customer needs and tailor their supply chain processes accordingly.
Overall, companies must carefully evaluate their unique business requirements, industry dynamics, and customer expectations to select and implement the most suitable supply chain strategy. While each approach has its strengths and weaknesses, successful companies often combine elements of different strategies to create a competitive advantage in the market.
Technology in Supply Chain Management
Technology plays a crucial role in shaping modern supply chain management practices. From enhancing visibility to optimizing decision-making, innovative technologies like IoT, blockchain, and AI have revolutionized the way businesses manage their supply chains.
Internet of Things (IoT), Supply chain management
IoT refers to the network of interconnected devices that collect and exchange data in real-time. In supply chain management, IoT devices like sensors and RFID tags are used to track the movement of goods, monitor inventory levels, and ensure timely deliveries. This technology provides real-time insights into the supply chain, enabling businesses to identify bottlenecks, improve efficiency, and enhance overall performance.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent way to record transactions across a decentralized network. In supply chain management, blockchain is used to create an immutable record of every transaction, from the sourcing of raw materials to the delivery of finished products. This enhances transparency, traceability, and trust among supply chain partners, reducing the risk of fraud and errors.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI encompasses a range of technologies like machine learning and predictive analytics that enable computers to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. In supply chain management, AI is used for demand forecasting, route optimization, risk management, and inventory management. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI systems can make accurate predictions, automate processes, and improve decision-making, ultimately leading to cost savings and operational efficiencies.
Supply Chain Risk Management
In the world of supply chain management, it is crucial to address and mitigate potential risks that could disrupt operations and affect overall efficiency. Let’s explore common risks in the supply chain, strategies for mitigating these risks, and the importance of resilience and flexibility in managing unforeseen disruptions.
Common Risks in the Supply Chain and Their Impact
- Supplier Reliability: Dependence on a single supplier can lead to delays or disruptions if they encounter issues.
- Logistical Challenges: Transportation delays, natural disasters, and other unforeseen events can impact the timely delivery of goods.
- Quality Control Issues: Defective products or subpar materials can lead to increased costs and damage to reputation.
- Market Volatility: Fluctuations in demand, prices, or regulations can affect supply chain stability.
Strategies for Mitigating Risks in the Supply Chain
- Diversification: Work with multiple suppliers to reduce reliance on a single source.
- Supply Chain Visibility: Implement technologies to track and monitor the entire supply chain for early detection of potential issues.
- Risk Assessment: Regularly assess and update risk management strategies to stay ahead of potential disruptions.
- Collaboration: Build strong relationships with suppliers, partners, and other stakeholders to foster a network of support in times of need.
Importance of Resilience and Flexibility
In today’s fast-paced business environment, having the ability to adapt to unforeseen disruptions is key to maintaining a competitive edge. By building resilience and flexibility into the supply chain, companies can better navigate challenges and emerge stronger on the other side.